Elementary cellular automaton
The simplest class of one-dimensional CA: two states (0/1), three-cell neighborhood (left, center, right).
Parameters: states, neighborhood size, Number of possible rules:
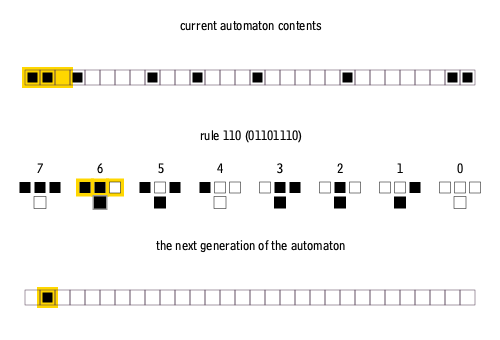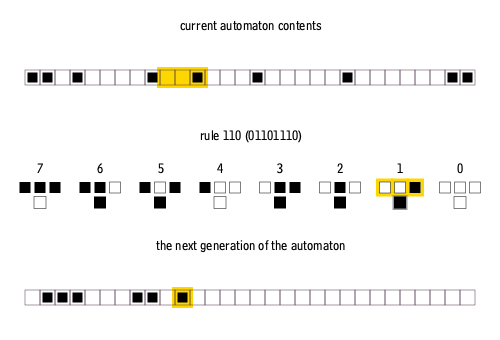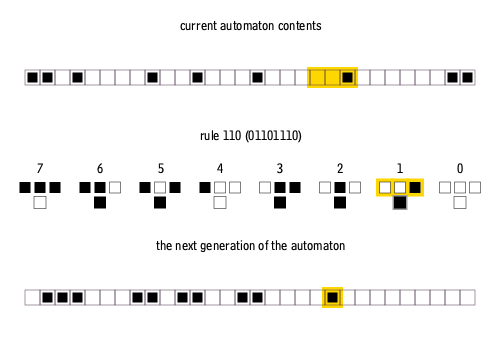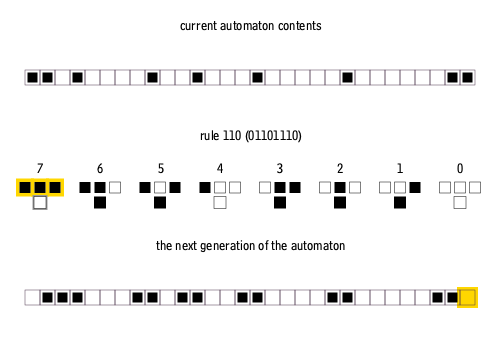
Each cell examines its left neighbor, itself, and its right neighbor - giving possible neighborhood configurations:
111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000
Each configuration maps to a new state (0 or 1) for the center cell:
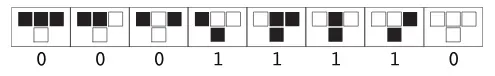
Rules are numbered using wolfram code, which encodes the rule’s behavior as a binary number read from the next-state outputs.
The -th bit (from right) of the Wolfram code specifies the next state when the neighborhood configuration equals in binary:
Current pattern 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 New state 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Reading the next states as binary:
01101110=
https://mathworld.wolfram.com/ElementaryCellularAutomaton.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rule_110
All 256 rules starting from a single black cell:
![[elementary CA-1762632781862.webp]]
![[elementary CA-1762632794076.webp]]
![[elementary CA-1762632805012.webp]]
![[elementary CA-1762632823043.webp]]
![[elementary CA-1762632658970.webp]]