A lognormal distribution is a statistical distribution characterised by a skewed bell-shaped curve. It arises, for instance, when taking the exponential of a normally distributed variable. It differs from a normal distribution in several ways. Most importantly, the curve of a normal distribution is symmetric, while the lognormal one is asymmetric with a heavy tail.
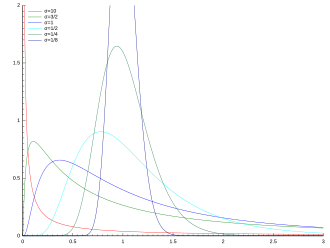
The lognormal distribution arises naturally as a result of multiplicative processes, similarly to how the normal distribution emerges when many independent variables are summed. 1
So if the distribution
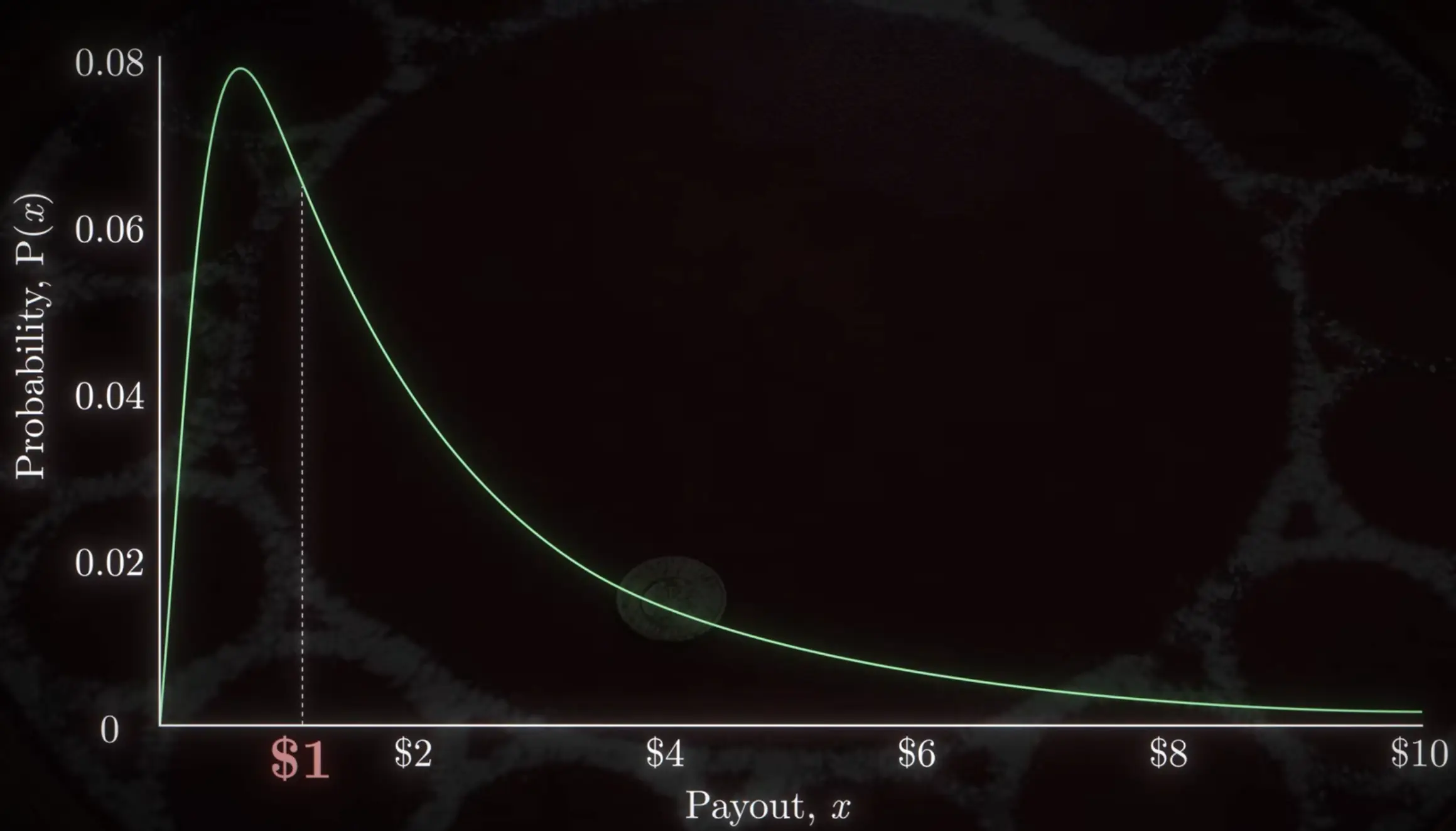
is plotted on a logarithmic x-axis, it resembles a normal distribution:
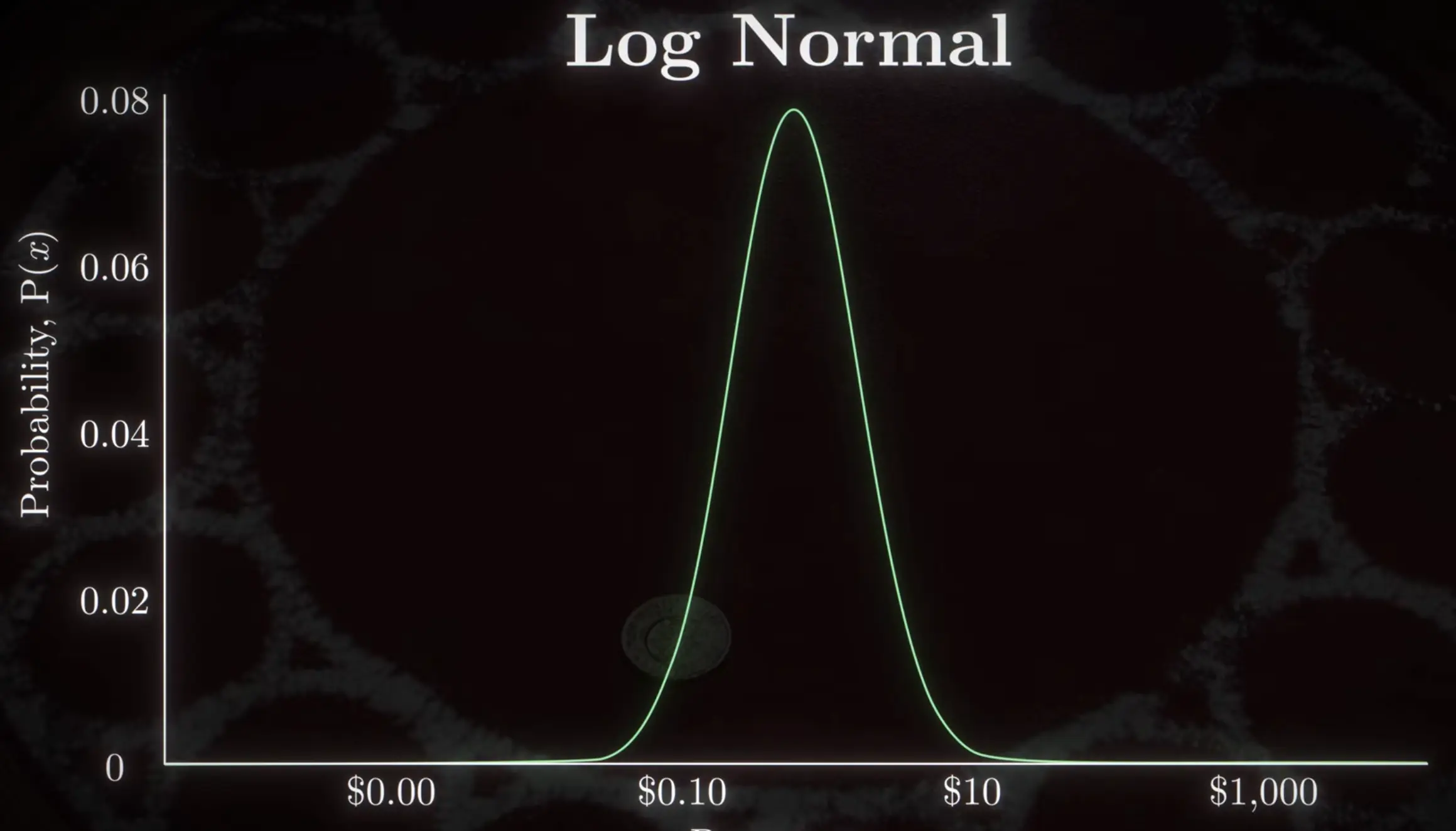
The distribution is asymmetric because the
Examples of lognormal distributions
- synaptic activity
- synaptic weights
- the number of connections a neuron has
- neuron firing rates
- the size of files on a computer
- the length of words in a language
- the size of living organisms
- the distribution of income
- the size of cities
- the size of companies