Astrocytes outnumber neurons 5:1 in the CNS.
Each astrocyte has its own domain of control in the CNS.
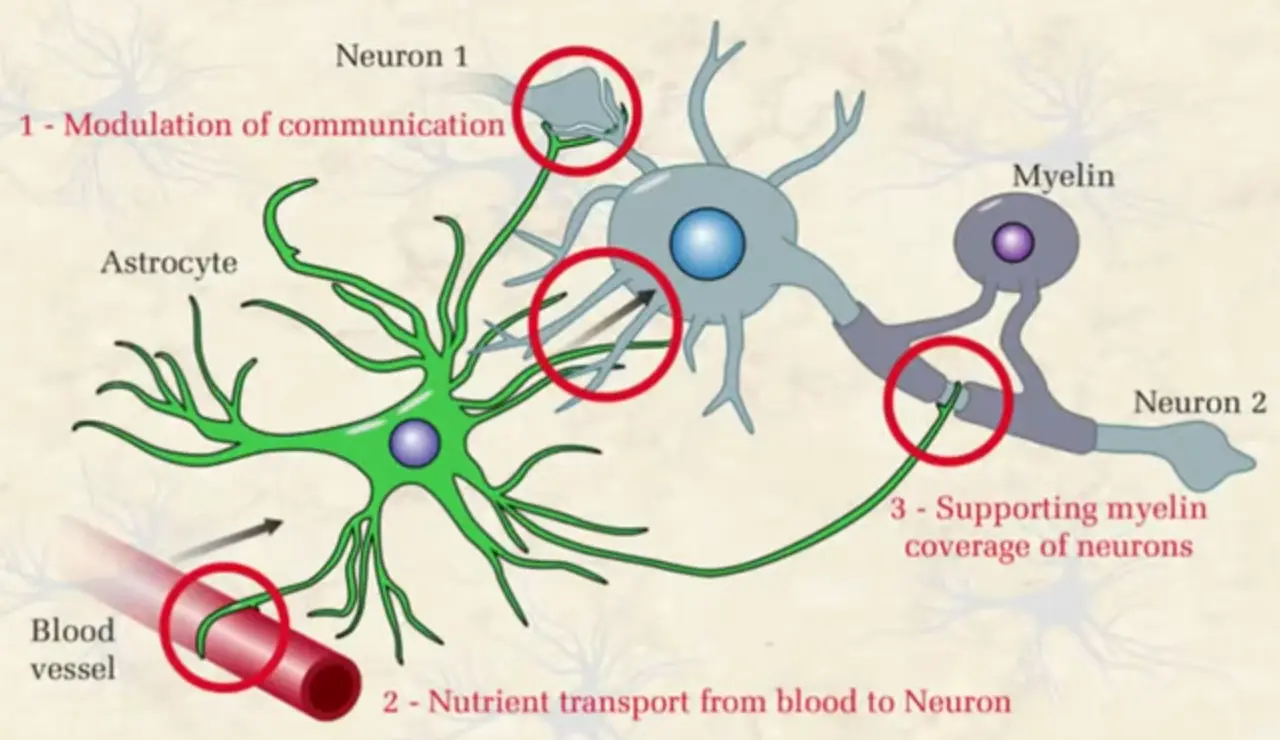
Astrocytes are important for supporting (the very sensitive and hungry) neurons in many ways.
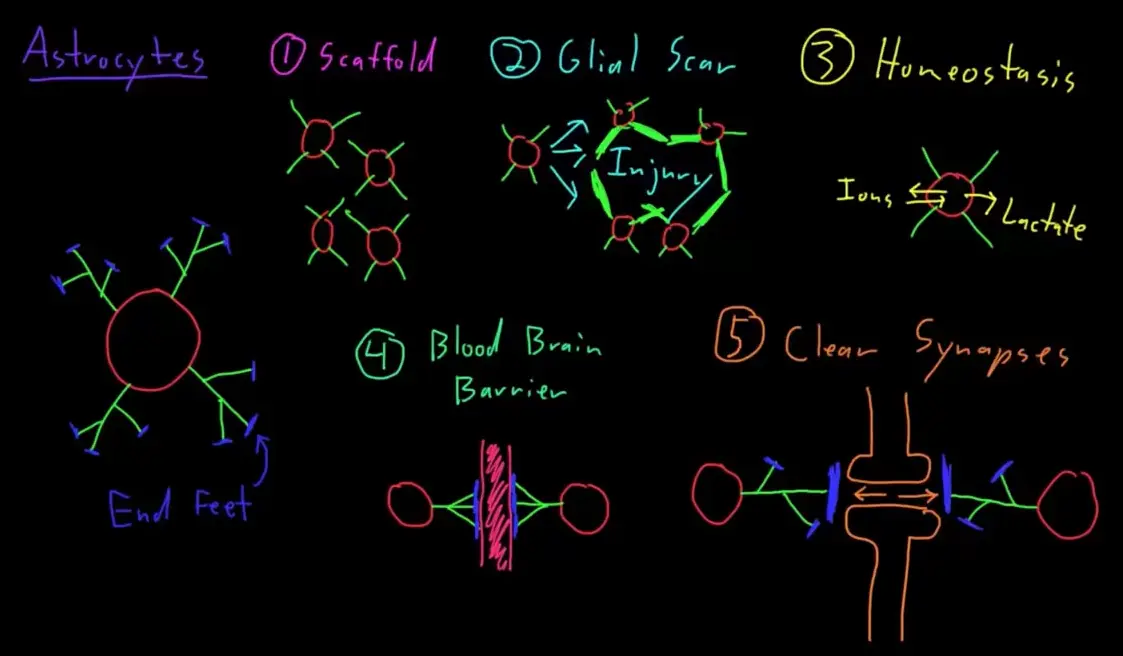
Astroctyes have a multitude of functions
- Scaffold: They occupy a large amount of the space in the CNS, and form a majority of the structure that makes up the brain and the spinal cord. This helps guide migrating developing axons, for example.
- Glial scar: They migrate to wounds to form a thick scar-like tissue.
- Homeostasis: They are constantly monitoring the interstitial fluid (fluid around cells) to keep the Ion concentrations the same. They can also lactate / secrete oxygen and glucose for neurons.
- Blood brain barrier: They prevent large, unwanted molecules entering the brain from blood vessels, by covering the blood vessels with their end feet.
- Clear Synapses: They surround synapses and basically reset them by clearing out neuro-tranmitters (molecules). Every synapse has an astrocyte
- They also influence neurons and other glia through an exchange of a variety of substances.
- They influence the migration of neurons in development.
- They get excited by Ca+ ions, which hints that they play a role in forming memories.
- They play a key role in the development of white matter.
In contrast to neurons, ther responses to stimuli are not all-or-nothing, but graded.
Info
Astrocytes are non-neuronal cells in the brain that have been traditionally overlooked but are now recognized as playing key roles in modulating brain networks. They integrate the activity of thousands of synapses and provide feedback to neurons by affecting their synaptic plasticity. Astrocytes are involved in modifying synaptic plasticity, facilitating switching between cognitive states, and tuning brain networks to operate near critical phase transitions. - Claude
References
Astrocytes | Nervous system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
TODO:
- Forebrain engraftment by human glial progenitor cells enhances synaptic plasticity and learning in adult mice
- A possible role of astrocytes in contextual memory retrieval: An analysis obtained using a quantitative framework
- Endocannabinoids potentiate synaptic transmission through stimulation of astrocytes
- Astrocytic activation generates de novo neuronal potentiation and memory enhancement
- Dysfunction of homeostatic control of dopamine by astrocytes in the developing prefrontal cortex leads to cognitive impairments
- Astrocyte-mediated spike-timing-dependent long-term depression modulates synaptic properties in the developing cortex
- Astroglial potassium clearance contributes to short-term plasticity of synaptically evoked currents at the tripartite synapse
- Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing–dependent depression at neocortical synapses
- ! Neuron-glia networks: integral gear of brain function
- ! Gliotransmitters Travel in Time and Space