Conditional probability
are two events (outcomes) of a random experiment. The probability of an event given that another event has occurred is:
If we know that has occured, becomes the new :
→
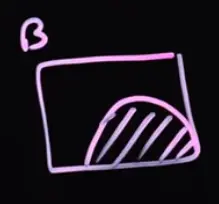
In this case, becomes a lot more likely, as it occupies a larger fraction of the sample space than it did before.
It’s easy to see geometrically: The reverse is not true (completely different proportions).