Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution with parameters (number of trials) and (probability of success on each trial) is a discrete probability distribution that describes the number of successes in a sequence of independent bernoulli experiments. Its PMF is given by
total number of Bernoulli events
number of “positive” events
probability of positive event
binomial coefficient – number of ways to choose successes from trials
Binomial random variable
A random variable that counts the number of successes in independent Bernoulli trials, each with probability of success , is called a binomial random variable:
When we write , it implies that the probability of taking the value is given by the PMF of the binomial distribution.
EXAMPLE
We can pull them apart because they are independent.
Note: The coefficients are
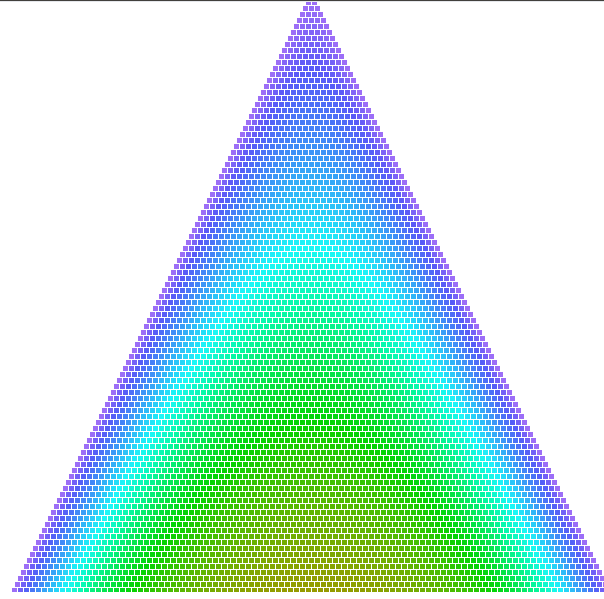
Link to originalPascals triangle (the binomial distribution) converges to the normal distribution for large .
At about , the normal distribution starts to be a very good approximation.
Computing is easier than computing the binomial distribution. Flipping a coin 400 times: calculating requires summing 41 binomial terms:
With normal approximation:
where is the probability of success, is the probability of failure, and is the number of trials.
This is true is not too small, i.e. success and failure are not too rare.
If they are, the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution, where is the average number of successes.See also Central Limit Theorem.