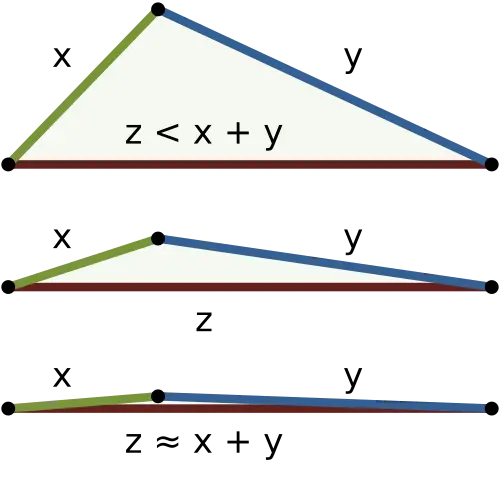
Triangle Inequality
For any triangle, the sum of the lenghts of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remainingg side:
With equality only in the degenerate case of a triangle with zero area.
→ The shortest distance between two points is a straight line.
Generally:This also translates to vector spaces with a norm:
, i.e. this equality holds if two vectors point in the same direction.
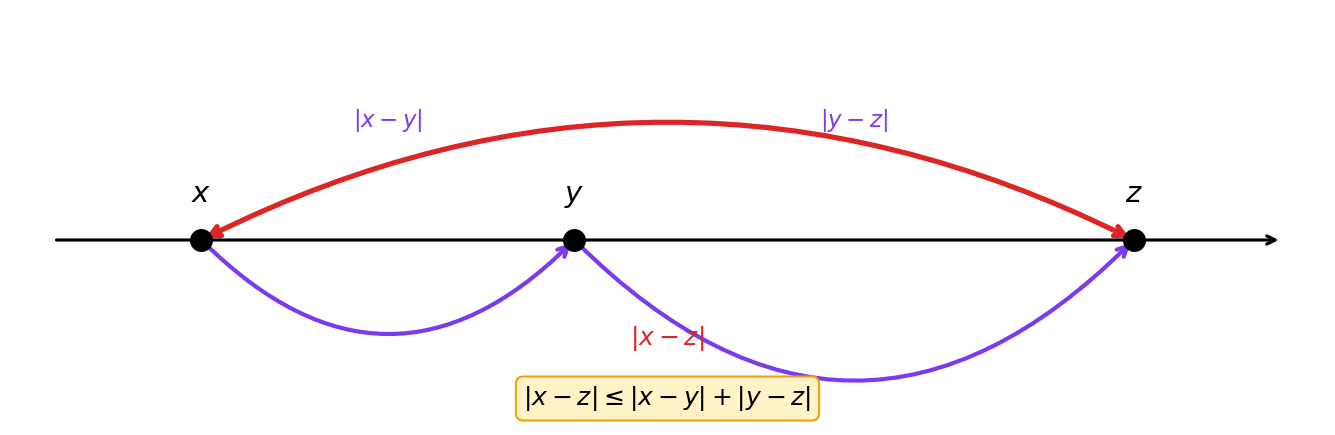
Absolute value as distance
On , is the distance between and . The direct distance from to is at most the distance going via any intermediate point :